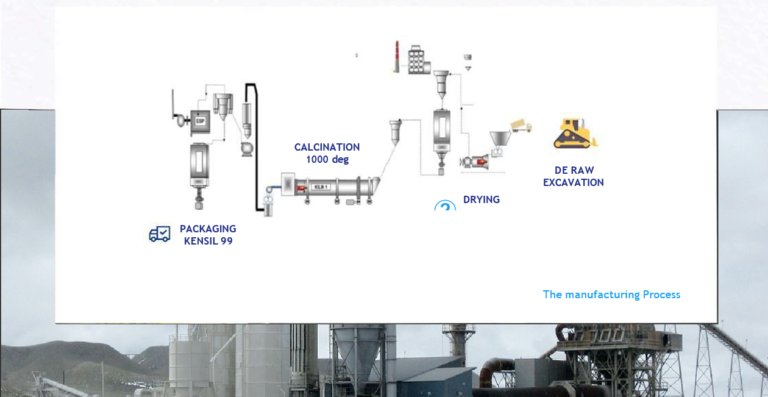
Our Process
The mining and processing of diatomite is delicate and complicated. It requires large processing facilities and heavy earth moving equipment. To minimize costs, diatomite is usually mined in open-pit, surface mines (although some operations do use underground extraction methods). In surface mining, a considerable thickness of earth, known as overburden, may have to be removed. Once this layer is removed and the purest of the diatomite strata is exposed, it is then cut from the bed with powerful scrapers and stockpiled. Diatomite does not need to be blastedas it is a so , friable ore.
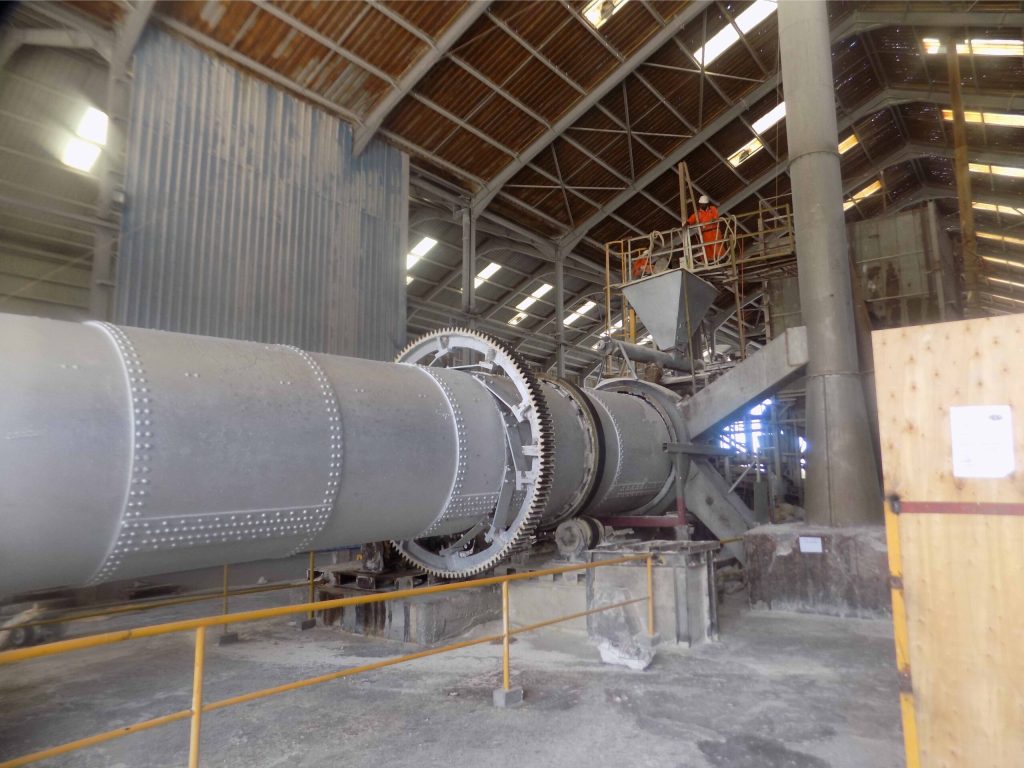
The stockpiled material is then hauled to the processing plant for crushing, drying, milling and o en calcining. Going into the crusher, the pieces may be as large as a small car, but coming out they will be the size of a pea.
At this point the ore will still contain moisture. In order to dry the ore, significant amounts of heat must be applied in flash dryers. The ore is then milled gently to preserve the structure. It is criticalthat the ore be completely pure. For most applications, the ore is then either calcined or flux calcined in a large rotary kiln to agglomerate the diatoms and produce the desired grade. This is a highly energy intensive process.
The ore is heated to temperatures in excess of 1100 degrees Centigrade with sodium carbonate added to improve the particle size distribution and make it white Finally, the material is classified to meet the specific customer needs, packaged and sent to customers.

